Before the next chapter explores testing on physical Android devices, this chapter will take some time to provide an overview of the Android Studio AVD emulator and highlight many of the configuration features available to customize the environment in both standalone and tool window modes.
The Emulator Environment
When launched in standalone mode, the emulator displays an initial splash screen during the loading process. Once loaded, the main emulator window appears, containing a representation of the chosen device type (in the case of Figure 5-1, this is a Pixel 4 device):
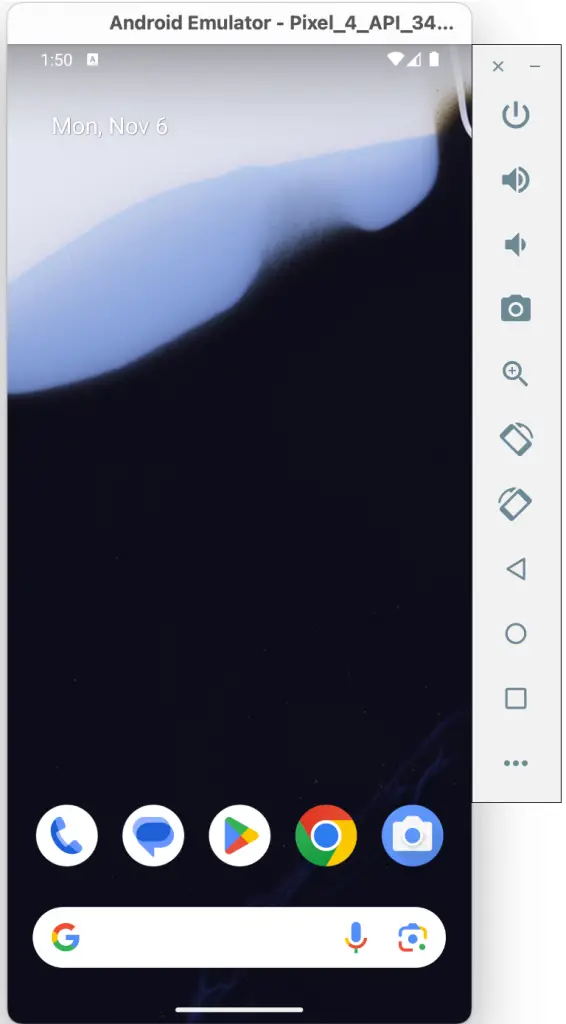
The toolbar positioned along the right-hand edge of the window provides quick access to the emulator controls and configuration options.
Emulator Toolbar Options
The emulator toolbar (Figure 5-2) provides access to a range of options relating to the appearance and behavior of the emulator environment.
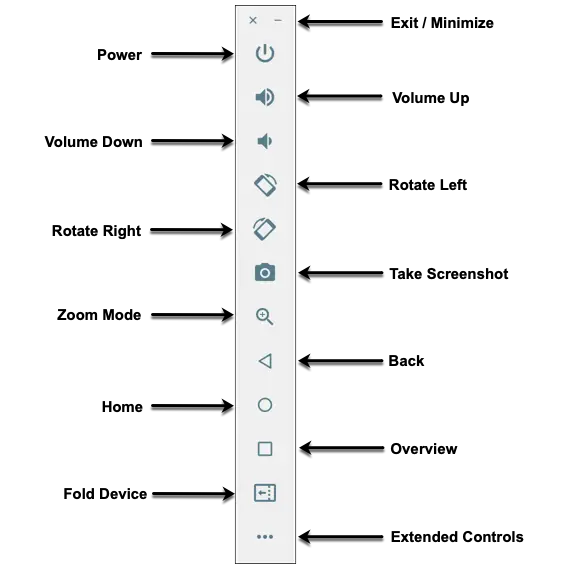
Each button in the toolbar has associated with it a keyboard accelerator which can be identified either by hovering the mouse pointer over the button and waiting for the tooltip to appear or via the help option of the extended controls panel.
Though many of the options contained within the toolbar are self-explanatory, each option will be covered for the sake of completeness:
- Exit / Minimize – The uppermost ‘x’ button in the toolbar exits the emulator session when selected, while the ‘-’ option minimizes the entire window.
- Power – The Power button simulates the hardware power button on a physical Android device. Clicking and releasing this button will lock the device and turn off the screen. Clicking and holding this button will initiate the device “Power off” request sequence.
- Volume Up / Down – Two buttons that control the audio volume of playback within the simulator environment.
- Rotate Left/Right – Rotates the emulated device between portrait and landscape orientations.
- Take Screenshot – Takes a screenshot of the content displayed on the device screen. The captured image is stored at the location specified in the Settings screen of the extended controls panel, as outlined later in this chapter.
- Zoom Mode – This button toggles in and out of zoom mode, details of which will be covered later in this chapter.
- Back – Performs the standard Android “Back” navigation to return to a previous screen.
- Home – Displays the device’s home screen.
- Overview – Simulates selection of the standard Android “Overview” navigation, which displays the currently running apps on the device.
- Fold Device – Simulates the folding and unfolding of a foldable device. This option is only available if the emulator is running a foldable device system image.
- Extended Controls – Displays the extended controls panel, allowing for the configuration of options such as simulated location and telephony activity, battery strength, cellular network type, and fingerprint identification.
Working in Zoom Mode
The zoom button located in the emulator toolbar switches in and out of zoom mode. When zoom mode is active, the toolbar button is depressed, and the mouse pointer appears as a magnifying glass when hovering over the device screen. Clicking the left mouse button will cause the display to zoom in relative to the selected point on the screen, with repeated clicking increasing the zoom level. Conversely, clicking the right mouse button decreases the zoom level. Toggling the zoom button off reverts the display to the default size.
Clicking and dragging while in zoom mode will define a rectangular area into which the view will zoom when the mouse button is released.
While in zoom mode, the screen’s visible area may be panned using the horizontal and vertical scrollbars located within the emulator window.
Resizing the Emulator Window
The emulator window’s size (and the device’s corresponding representation) can be changed at any time by enabling Zoom mode and clicking and dragging on any of the corners or sides of the window.
Extended Control Options
The extended controls toolbar button displays the panel illustrated in Figure 5-3. By default, the location settings will be displayed. Selecting a different category from the left-hand panel will display the corresponding group of controls:
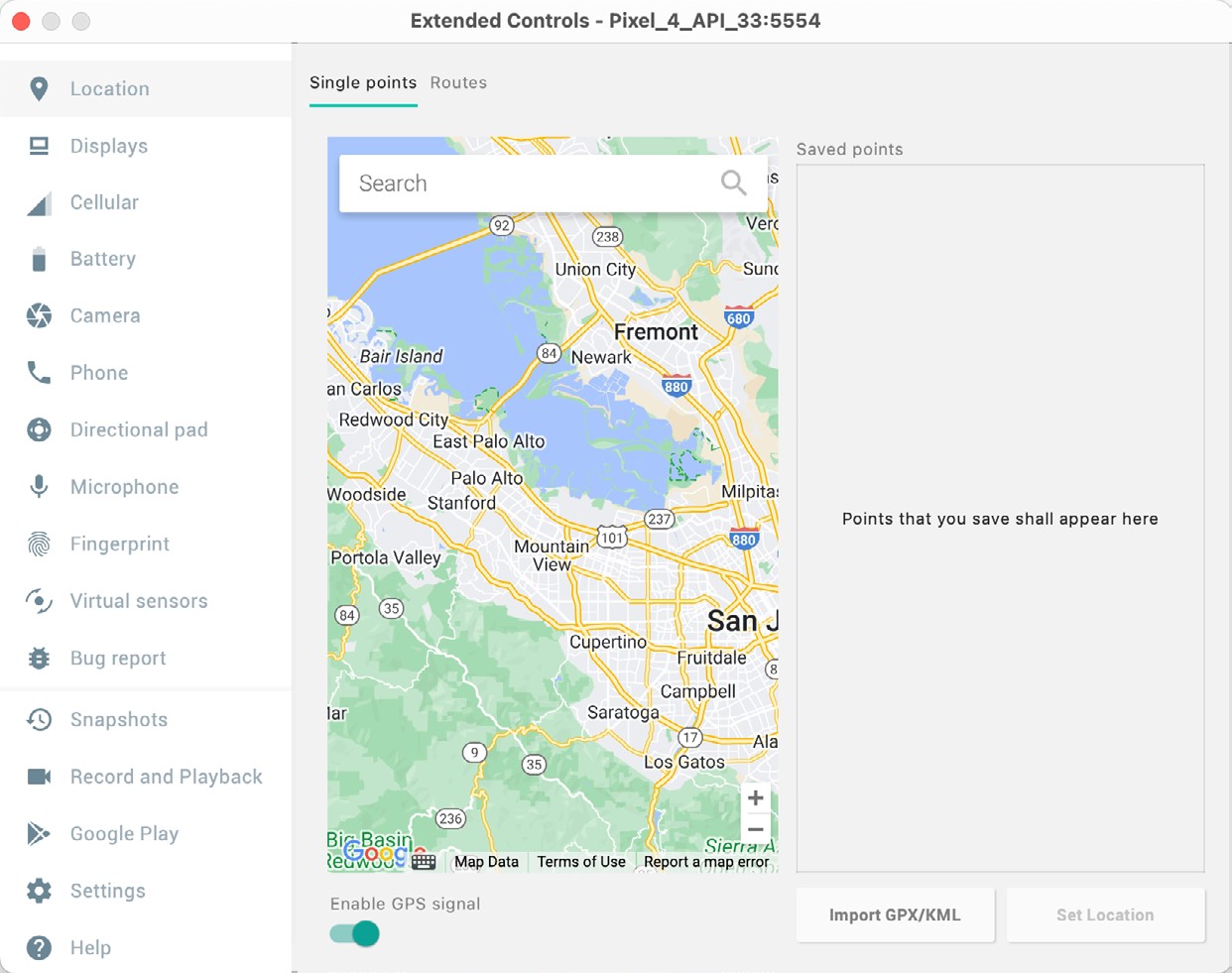
Location
The location controls allow simulated location information to be sent to the emulator as decimal or sexigesimal coordinates. Location information can take the form of a single location or a sequence of points representing the device’s movement, the latter being provided via a file in either GPS Exchange (GPX) or Keyhole Markup Language (KML) format. Alternatively, the integrated Google Maps panel may be used to select single points or travel routes visually.
Displays
In addition to the main display shown within the emulator screen, the Displays option allows additional displays to be added running within the same Android instance. This can be useful for testing apps for dual-screen devices such as the Microsoft Surface Duo. These additional screens can be configured to be any required size and appear within the same emulator window as the main screen.
Cellular
The type of cellular connection being simulated can be changed within the cellular settings screen. Options are available to simulate different network types (CSM, EDGE, HSDPA, etc.) in addition to a range of voice and data scenarios, such as roaming and denied access.
Battery
Various battery state and charging conditions can be simulated on this panel of the extended controls screen, including battery charge level, battery health, and whether the AC charger is currently connected.
Camera
The emulator simulates a 3D scene when the camera is active. This takes the form of the interior of a virtual building through which you can navigate by holding down the Option key (Alt on Windows) while using the mouse pointer and keyboard keys when recording video or before taking a photo within the emulator. This extended configuration option allows different images to be uploaded for display within the virtual environment.
Phone
The phone extended controls provide two straightforward but helpful simulations within the emulator. The first option simulates an incoming call from a designated phone number. This can be particularly useful when testing how an app handles high-level interrupts.
The second option allows the receipt of text messages to be simulated within the emulator session. As in the real world, these messages appear within the Message app and trigger the standard notifications within the emulator.
Directional Pad
A directional pad (D-Pad) is an additional set of controls either built into an Android device or connected externally (such as a game controller) that provides directional controls (left, right, up, down). The directional pad settings allow D-Pad interaction to be simulated within the emulator.
Microphone
The microphone settings allow the microphone to be enabled and virtual headset and microphone connections to be simulated. A button is also provided to launch the Voice Assistant on the emulator.
Fingerprint
Many Android devices are now supplied with built-in fingerprint detection hardware. The AVD emulator makes it possible to test fingerprint authentication without the need to test apps on a physical device containing a fingerprint sensor. Details on configuring fingerprint testing within the emulator will be covered later in this chapter.
Virtual Sensors
The virtual sensors option allows the accelerometer and magnetometer to be simulated to emulate the effects of the physical motion of a device, such as rotation, movement, and tilting through yaw, pitch, and roll settings.
Snapshots
Snapshots contain the state of the currently running AVD session to be saved and rapidly restored, making it easy to return the emulator to an exact state. Snapshots are covered later in this chapter.
Record and Playback
Allows the emulator screen and audio to be recorded and saved in WebM or animated GIF format.
Google Play
If the emulator is running a version of Android with Google Play Services installed, this option displays the current Google Play version. It also provides the option to update the emulator to the latest version.
Settings
The settings panel provides a small group of configuration options. Use this panel to choose a darker theme for the toolbar and extended controls panel, specify a file system location into which screenshots are to be saved, configure OpenGL support levels, and configure the emulator window to appear on top of other windows on the desktop.
Help
The Help screen contains three sub-panels containing a list of keyboard shortcuts, links to access the emulator online documentation, file bugs and send feedback, and emulator version information.
Working with Snapshots
When an emulator starts for the first time, it performs a cold boot, much like a physical Android device when powered on. This cold boot process can take some time to complete as the operating system loads and all the background processes are started. To avoid the necessity of going through this process every time the emulator is started, the system is configured to automatically save a snapshot (referred to as a quick-boot snapshot) of the emulator’s current state each time it exits. The next time the emulator is launched, the quick-boot snapshot is loaded into memory, and execution resumes from where it left off previously, allowing the emulator to restart in a fraction of the time needed for a cold boot to complete.
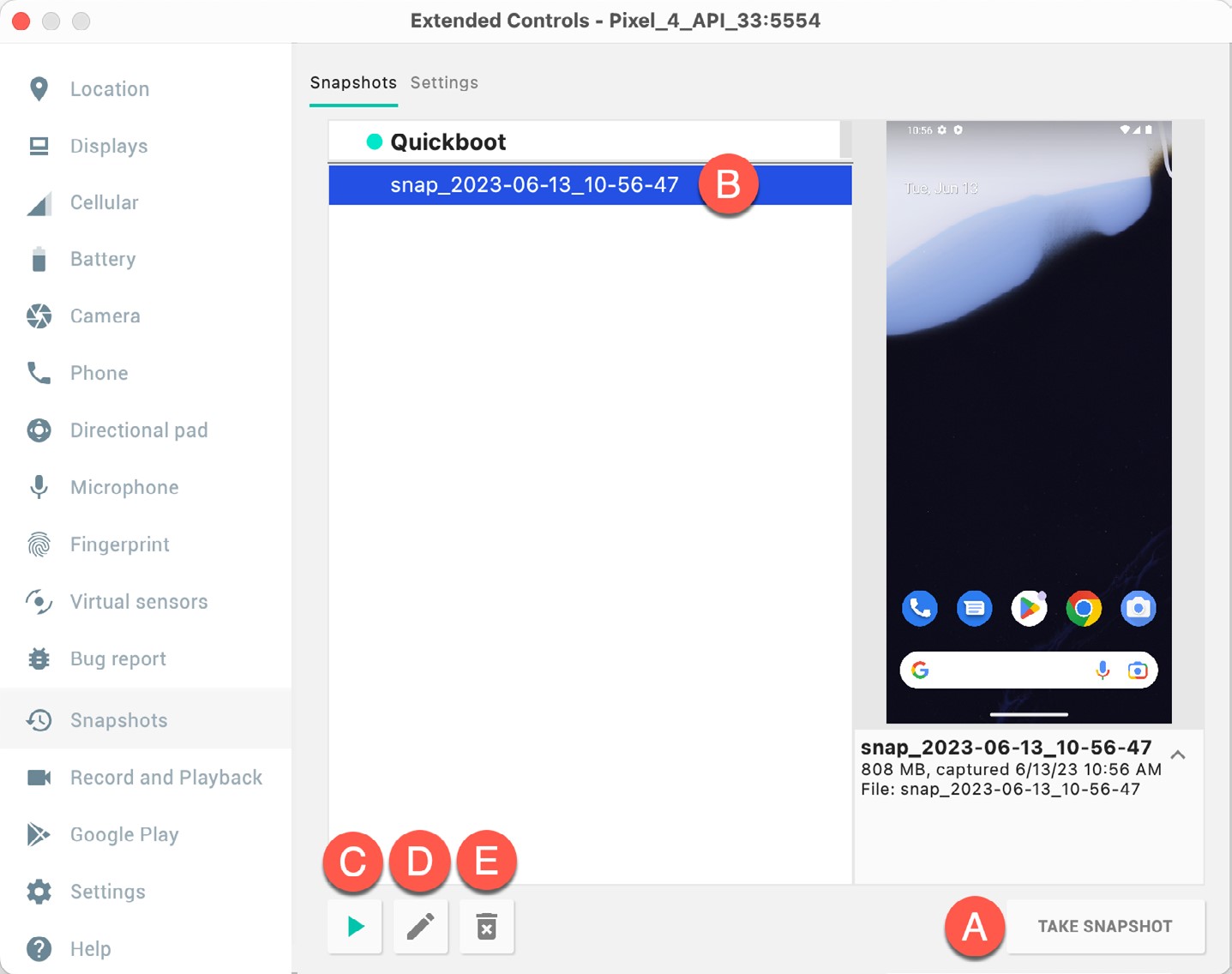
The Snapshots screen of the extended controls panel can store additional snapshots at any point during the execution of the emulator. This saves the exact state of the entire emulator allowing the emulator to be restored to the exact point in time that the snapshot was taken. From within the screen, snapshots can be taken using the Take Snapshot button (marked A in Figure 5-4). To restore an existing snapshot, select it from the list (B) and click the run button (C) located at the bottom of the screen. Options are also provided to edit (D) the snapshot name and description and to delete (E) the currently selected snapshot:
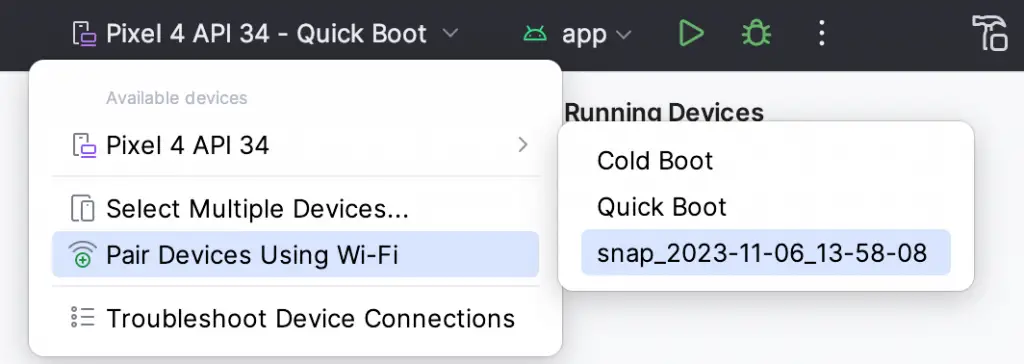
You can also choose whether to start an emulator using either a cold boot, the most recent quick-boot snapshot, or a previous snapshot by making a selection from the run target menu in the main toolbar, as illustrated in Figure 5-5:
Configuring Fingerprint Emulation
The emulator allows up to 10 simulated fingerprints to be configured and used to test fingerprint authentication within Android apps. Configuring simulated fingerprints begins by launching the emulator, opening the Settings app, and selecting the Security option.
Within the Security settings screen, select the fingerprint option. On the resulting information screen, click on the Next button to proceed to the Fingerprint setup screen. Before fingerprint security can be enabled, a backup screen unlocking method (such as a PIN) must be configured. Enter and confirm a suitable PIN and complete the PIN entry process by accepting the default notifications option.
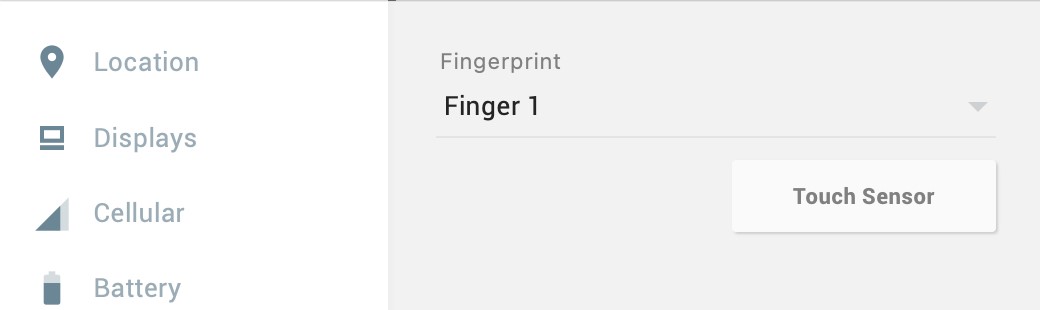
Proceed through the remaining screens until the Settings app requests a fingerprint on the sensor. At this point, display the extended controls dialog, select the Fingerprint category in the left-hand panel, and make sure that Finger 1 is selected in the main settings panel:
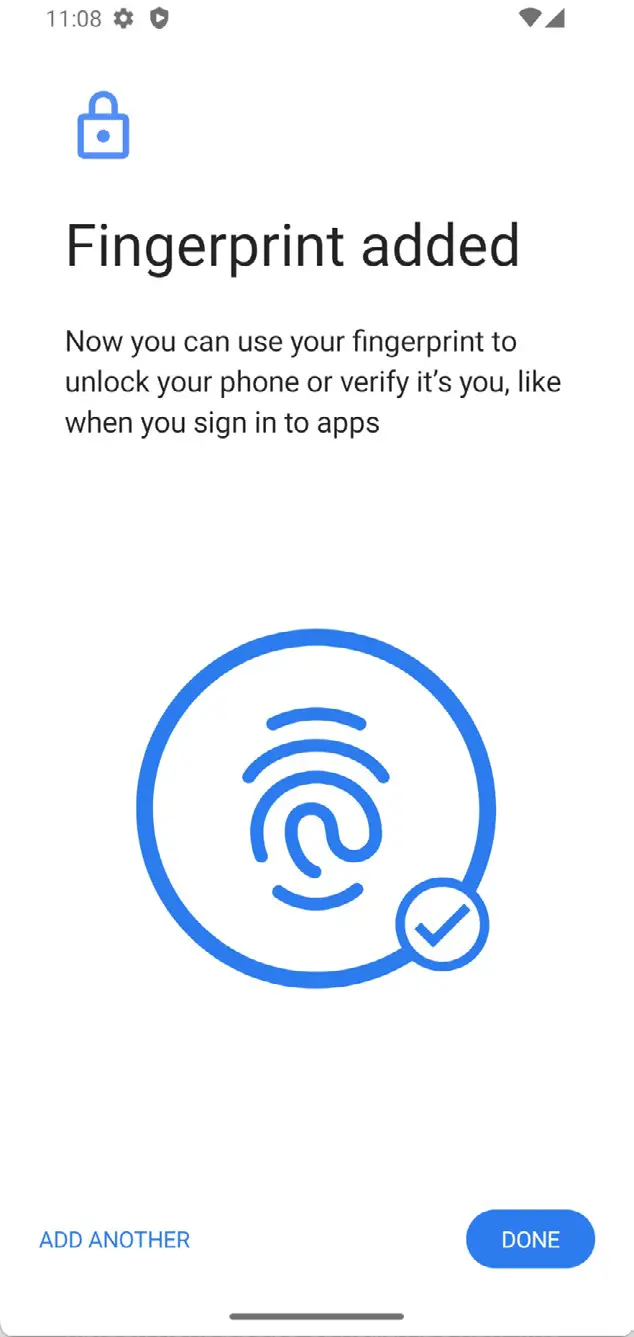
Click on the Touch Sensor button to simulate Finger 1 touching the fingerprint sensor. The emulator will report the successful addition of the fingerprint:
To add additional fingerprints, click on the Add Another button and select another finger from the extended controls panel menu before clicking on the Touch Sensor button again.
The Emulator in Tool Window Mode
As outlined in the previous chapter (Creating an Android Virtual Device (AVD) in Android Studio), Android Studio can be configured to launch the emulator in an embedded tool window so that it does not appear in a separate window. When running in this mode, the same controls available in standalone mode are provided in the toolbar, as shown in Figure 5-8:
From left to right, these buttons perform the following tasks (details of which match those for standalone mode):
- Power
- Volume Up
- Volume Down
- Rotate Left
- Rotate Right
- Back
- Home
- Overview
- Screenshot
- Snapshots
- Extended Controls
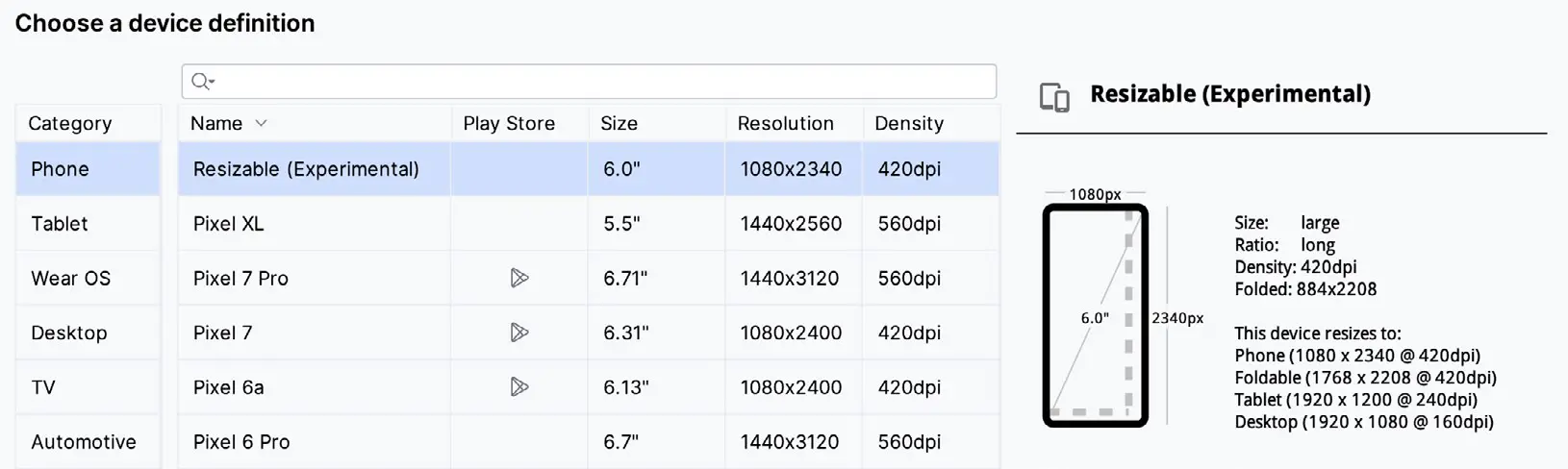
Creating a Resizable Emulator
In addition to emulators configured to match specific Android device models, Android Studio also provides a resizable AVD that allows you to switch between phone, tablet, and foldable device sizes. To create a resizable emulator, open the Device Manager and click the ‘+’ toolbar. Next, select the Resizable device definition illustrated in Figure 5-9, and follow the usual steps to create a new AVD:
When you run an app on the new emulator within a tool window, the Display mode option will appear in the toolbar, allowing you to switch between emulator configurations as shown in Figure 5-10:
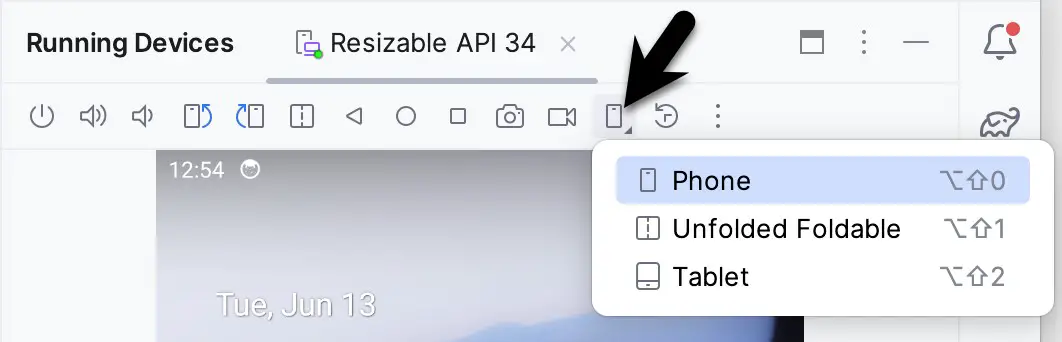
If the emulator is running in standalone mode, the Display mode option can be found in the side toolbar, as shown below:

Summary
Android Studio contains an Android Virtual Device emulator environment designed to make it easier to test applications without running them on a physical Android device. This chapter has provided a brief tour of the emulator and highlighted key features available to configure and customize the environment to simulate different testing conditions.

