In the preceding chapters, we spent some time looking at handling raw geographical location information in the form of longitude, latitude, and altitude data. The next step is to learn about the presentation of location information to the user through maps and satellite images. Therefore, this chapter aims to provide an overview of the steps necessary to present the app user with location, map, and satellite imagery using the MapKit Framework and, in particular, the MKMapView class. This example app will be extended in the next chapters to use the Map Kit local search and directions features.
About the MapKit Framework
The MapKit Framework is based on the Apple Maps data and APIs and provides iOS developers with a simple mechanism for integrating detailed and interactive mapping capabilities into any app.
The core element of the MapKit Framework from the point of view of the app developer is the MKMapView class. This class is a subclass of UIView and provides a canvas onto which map and satellite information may be presented to the user. Information may be presented in map, satellite, or hybrid (whereby the map is superimposed onto the satellite image) form. The displayed geographical region may be changed manually by the user via a process of pinching, stretching, and panning gestures or programmatically from within the app code via method calls and property manipulation on the MkMapView instance. The device’s current location may also be displayed and tracked on the map view.
The MapKit Framework also includes support for adding annotations to a map. This takes the form of a pin or custom image, title, and subview that may be used to mark specific locations on a map. Alternatively, the annotation can take the form of a custom view controller.
Implementation of the MKMapViewDelegate protocol allows an app to receive notifications of events relating to the map view, such as a change in either the user’s location or region of the map displayed or the failure of the device to identify the user’s current location or to download map data.
Understanding Map Regions
The area of the map that is currently displayed to the user is referred to as the region. This is defined in terms of a center location (declared by longitude and latitude) and the span of the surrounding area to be displayed. Adjusting the span has the effect of zooming in and out of the map relative to the specified center location. The region’s span may be specified using either distance (in meters) or coordinate-based degrees. When using degrees, one degree of latitude is equivalent to 111 km. Latitude, however, varies depending on the longitudinal distance from the equator. Given this complexity, the map view tutorial in this chapter will declare the span in terms of distance.
Getting Transit ETA Information
A MapKit feature introduced in iOS 9 allows the departure and arrival times and estimated travel duration to a destination using public transit to be obtained from within an iOS app. This involves the use of MKDirections. Request object configured for travel by transit and initialized with start and end locations combined with a call to the calculateETA(completionHandler:) method of an appropriately configured MKDirections instance. The following method, for example, outputs the estimated arrival time for a journey by transit from the Empire State Building in New York to JFK Airport:
func getTransitETA() {
let request = MKDirections.Request()
let source = MKMapItem(placemark:
MKPlacemark(coordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 40.748384,
longitude: -73.985479), addressDictionary: nil))
source.name = "Empire State Building"
request.source = source
let destination = MKMapItem(placemark:
MKPlacemark(coordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 40.643351,
longitude: -73.788969), addressDictionary: nil))
destination.name = "JFK Airport"
request.destination = destination
request.transportType = MKDirectionsTransportType.transit
let directions = MKDirections(request: request)
directions.calculateETA {
(response, error) -> Void in
if error == nil {
if let estimate = response {
print("Travel time \(estimate.expectedTravelTime / 60)")
print("Departing at \(estimate.expectedDepartureDate)")
print("Arriving at \(estimate.expectedArrivalDate)")
}
}
}
}Code language: Swift (swift)About the MKMapView Tutorial
This tutorial aims to develop an iOS app to display a map with a marker indicating the user’s current location. In addition, buttons in a navigation bar are provided to allow the user to zoom in on the current location and toggle between map and satellite views. Through the implementation of the MKMapViewDelegate protocol, the map will update as the user’s location changes so that the current location marker is always the center point of the displayed map region.
Creating the Map Project
Begin by launching Xcode and creating a new Xcode project using the iOS App template with the Swift and Storyboard options selected, entering MapSample as the product name.
Adding the Navigation Controller
The later stages of this tutorial will require the services of a navigation controller. Since the presence of the navigation bar will have implications for the layout of the user interface of the main view, it makes sense to add the controller now. Select the Main.storyboard file from the project navigator panel followed by the view controller view so that it highlights in blue and use the Editor -> Embed In -> Navigation Controller menu option to embed a controller into the storyboard as illustrated in Figure 68-1:
Creating the MKMapView Instance and Toolbar
The next step is to create an instance of the MKMapView class we will be using in our app and to add a toolbar instance to the user interface. Remaining in the Main.storyboard file, drag a Toolbar from the Library panel and place it at the bottom of the view canvas.
Next, drag and drop a Map Kit View object onto the canvas and resize and position it so that it takes up the remaining space in the view above the toolbar and below the navigation bar. By default, the Interface Builder tool will have added a single Bar Button Item to the new toolbar. However, two buttons will be required for this example, so drag and drop a second Bar Button Item from the Library panel onto the toolbar. Double-click on the toolbar button items and change the text to “Zoom” and “Type,” respectively:

Select the MKMapView object in the scene and use the Auto Layout Add New Constraints menu in the lower right-hand corner of the Interface Builder panel to configure Spacing to nearest neighbor constraints of 0 on all four sides of the view with the Constrain to margins option switched off. Once the four constraints have been added to the MKMapView object, repeat these steps with the Toolbar view selected, this time with the bottom value set to 21.
Select the MKMapView object in the view canvas, display the Assistant Editor and verify that the editor is displaying the contents of the ViewController.swift file. Ctrl-click on the MKMapView object and drag it to a position below the class declaration line in the Assistant Editor. Release the line, and in the resulting connection dialog, establish an outlet connection named mapView.
Click on the “Zoom” button to select it (note that to select a toolbar button item, it may be necessary to click on it twice since the first click selects the toolbar parent). With the button item selected, Ctrl-click on the button object and drag the line to the area immediately beneath the viewDidLoad method in the Assistant Editor panel. Release the line and, within the resulting connection dialog, establish an Action method on the Touch Up Inside event configured to call a method named zoomIn. Repeat this step to connect the “Type” button to a method named changeMapType.
Select the ViewController.swift file from the project navigator panel and verify that the outlets and actions have been set up correctly. Also, take this opportunity to import the MapKit framework and declare the class as implementing the MKMapViewDelegate protocol:
import UIKit
import MapKit
class ViewController: UIViewController, MKMapViewDelegate {
@IBOutlet weak var mapView: MKMapView!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
}
@IBAction func zoomIn(_ sender: Any) {
}
@IBAction func changeMapType(_ sender: Any) {
}
.
.
.
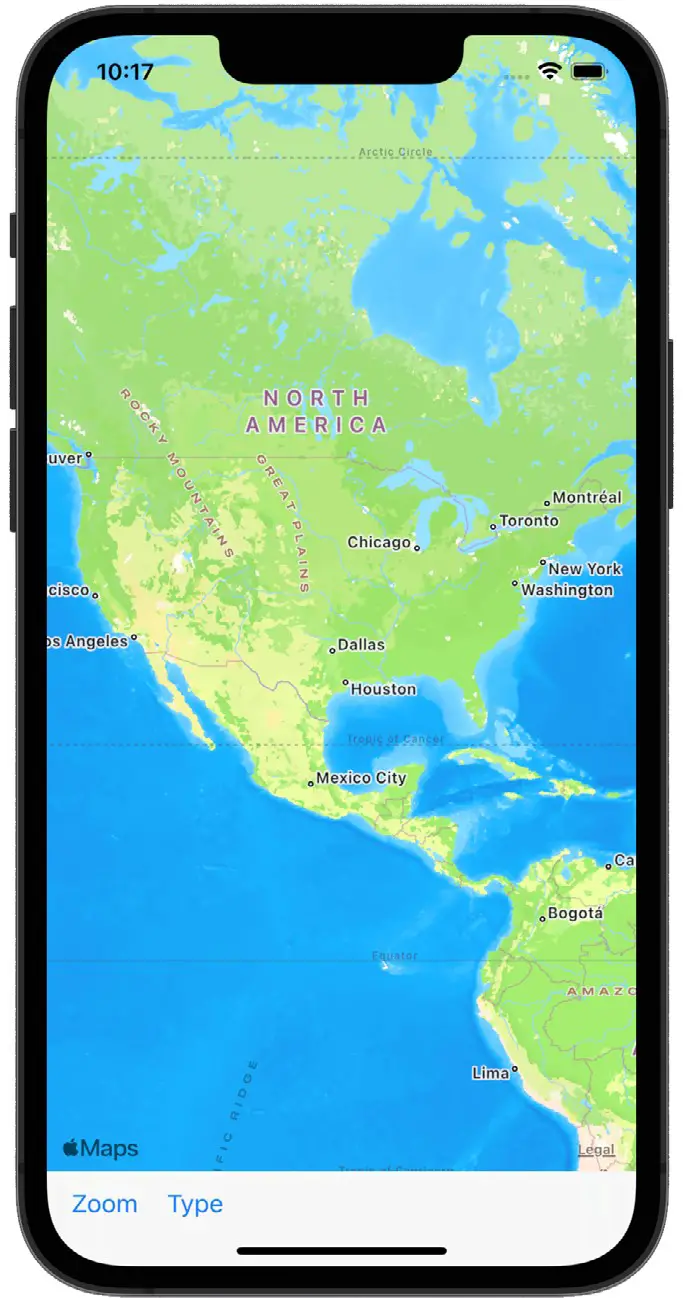
}Code language: Swift (swift)Perform a test run of the app’s progress by clicking on the run button in the Xcode toolbar. The app should run on the iOS simulator or device as illustrated in Figure 68-3:
Obtaining Location Information Permission
The next task is to request permission from the user to track the device’s current location. Since this needs to occur when the app loads, an ideal location is in the app delegate didFinishLaunchingWithOptions method in the AppDelegate.swift file:
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
@main
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var locationManager: CLLocationManager?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions
launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
locationManager = CLLocationManager()
locationManager?.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
return true
}
.
.
}Code language: Swift (swift)Setting up the Usage Description Keys
The above code changes included a method call to request permission from the user to track location information when the app is running in the foreground. This method call must be accompanied by the usage description strings, which need to be added to the project’s Info.plist file. To add this entry, select the Location entry at the top of the Project navigator panel and select the Info tab in the main panel. Next, click on the + button contained with the last line of properties in the Custom iOS Target Properties section. Then, select the Privacy – Location When in Use Usage Description item from the resulting menu. Once the key has been added, double-click in the corresponding value column and enter the following text:
This information is required to show your current locationCode language: plaintext (plaintext)Repeat this step, this time adding a Privacy – Location Always and When In Use Usage Description key set to the following string value:
Always mode is recommended for this app for improved location trackingCode language: plaintext (plaintext)Configuring the Map View
By default, the Map View does not indicate the user’s current location. By setting the showsUserLocation property of the MKMapView class, the map is instructed to display a representation of the current location on the map in the form of a blue marker. Before user location information can be obtained, it is first necessary to seek permission from the user. To achieve these goals, select the ViewController.swift file and locate and modify the viewDidLoad method as follows:
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
mapView.showsUserLocation = true
}Code language: Swift (swift)Changing the MapView Region
When the user taps the Zoom button, the map view region needs to be changed so that the user’s current location is set as the central location and the region span needs to be changed to 2000 meters (analogous to zooming in to the map region). The code to implement this belongs in the zoomIn method, which now needs to be implemented in the ViewController.swift file:
@IBAction func zoomIn(_ sender: Any) {
if let userLocation = mapView.userLocation.location?.coordinate {
let region = MKCoordinateRegion(
center: userLocation, latitudinalMeters: 2000,
longitudinalMeters: 2000)
mapView.setRegion(region, animated: true)
}
}Code language: Swift (swift)This method performs some very simple operations to achieve the desired effect in the mapView object. First, the user’s current location coordinates are ascertained by accessing the userLocation property of the map view object, which, in turn, contains the user’s coordinates. Next, the MKCoordinateRegionMakeWithDistance function is called to generate an MKCoordinateRegion object consisting of the user’s location coordinates and a span that stretches 2000 meters to the North and South of the current location. Finally, this region object is passed through to the setRegion method of the mapView object.
Now that the Zoom functionality has been implemented, it is time to configure the map type switching feature of the app.
Changing the Map Type
The object’s mapType property controls the map type of a map view. Supported values for this property are MKMapType.standard, MKMapType.mutedStandard, MKMapType.satellite MKMapType.hybrid, MKMapType.satelliteFlyover, and MKMapType.hybridFlyover. The map will switch between standard and satellite modes for this example app. Within the ViewController.swift file, modify the changeMapType action method connected to the Type button as follows:
@IBAction func changeMapType(_ sender: Any) {
if mapView.mapType == MKMapType.standard {
mapView.mapType = MKMapType.satellite
} else {
mapView.mapType = MKMapType.standard
}
}Code language: Swift (swift)This simple method toggles between the two map types when the user taps the button.
Testing the MapView App
Now that more functionality has been implemented, it is a good time to build and run the app again, so click on the Xcode Run button to load it into the iOS Simulator. Once the app has loaded, a blue dot should appear over Northern California. Since the app is running in the simulator environment, the location information is simulated to match either the coordinates of Apple’s headquarters in Cupertino, CA, or another simulated location depending on the current setting of the Debug -> Location menu.
Select the Type button to display the satellite view and then zoom in to get a better look at the region:
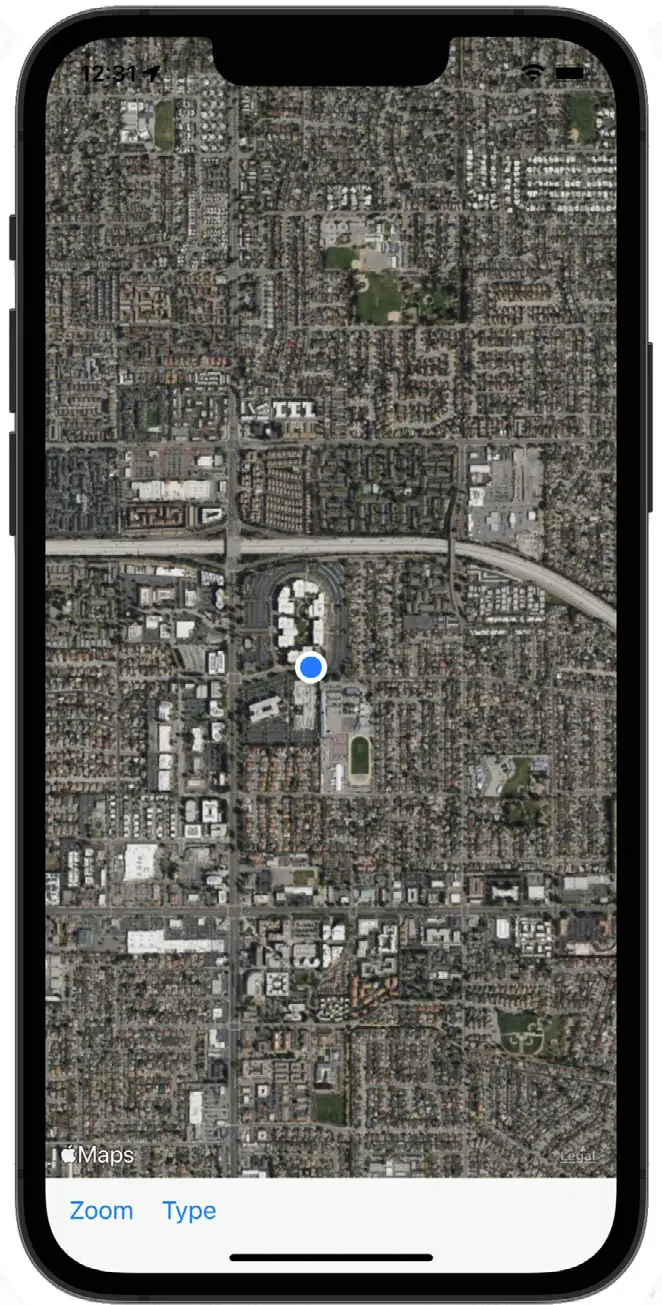
Load the app onto a physical iOS device to get real location information.
Updating the Map View based on User Movement
Assuming that you installed the app on a physical iOS device and went somewhere with the device in your possession (or used one of the debug location settings that simulated movement), you may have noticed that the map did not update as your location changed and that the blue dot marking your current location eventually went off the screen (also assuming, of course, that you had zoomed in to a significant degree).
To configure the app so the map automatically tracks the user’s movements, the first step is to ensure the app is notified when the location changes. At the start of this tutorial, the view controller was declared as conforming to the MKMapViewDelegate delegate protocol. One method that comprises this protocol is the mapView(didUpdate userLocation:) method. When implemented, this method is called by the map view object whenever the location of the device changes. We must, therefore, first specify that the MapSampleViewController class is the delegate for the mapView object, which can be performed by adding the following line to the viewDidLoad method located in the ViewController.swift file:
mapView.delegate = selfCode language: Swift (swift)The next task involves the implementation of the mapView(didUpdate userLocation:) method in the ViewController.swift file:
func mapView(_ mapView: MKMapView, didUpdate
userLocation: MKUserLocation) {
mapView.centerCoordinate = userLocation.location!.coordinate
}Code language: Swift (swift)The delegate method is passed as an argument to an MKUserLocation object containing the current location coordinates of the user. This value is assigned to the center coordinate property of the mapView object such that the current location remains at the region’s center. When the app is installed and run on a device, the current location will no longer move outside the displayed region as the device location changes. To experience this effect within the simulator, select the Features -> Location -> Freeway Drive menu option and then select the Zoom button in the user interface.
Summary
This chapter has demonstrated the basics of using the MKMapView class to display map-based information to the user within an iOS 17 app. The example created in the chapter also highlighted the steps involved in zooming into a map region, changing the map display type, and configuring a map to track the user’s current location.
The next chapter will explore the use of the local search feature of the MapKit Framework before extending the example app to mark all the locations of a specified business type on the map.

